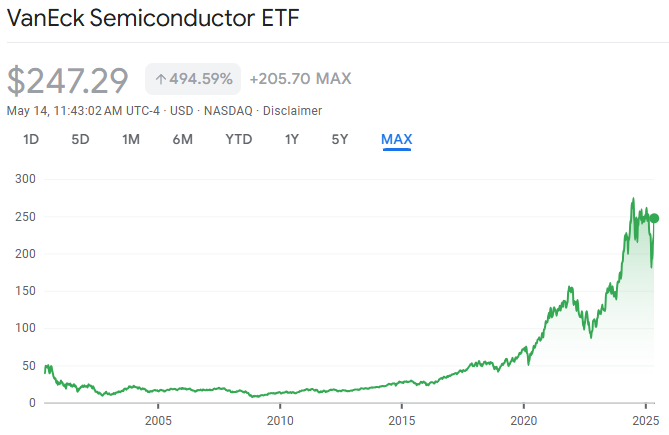
🙋♂️ Which S&P 500 ETF is actually the smartest choice?
SPY, VOO, IVV… aren’t they all basically the same?
It’s a fair question — and one every investor has probably asked.
While these ETFs do track the same index, they’re not identical.
Their fee structures, fund design, tax efficiency, trading volume, and even public perception vary more than you might think.
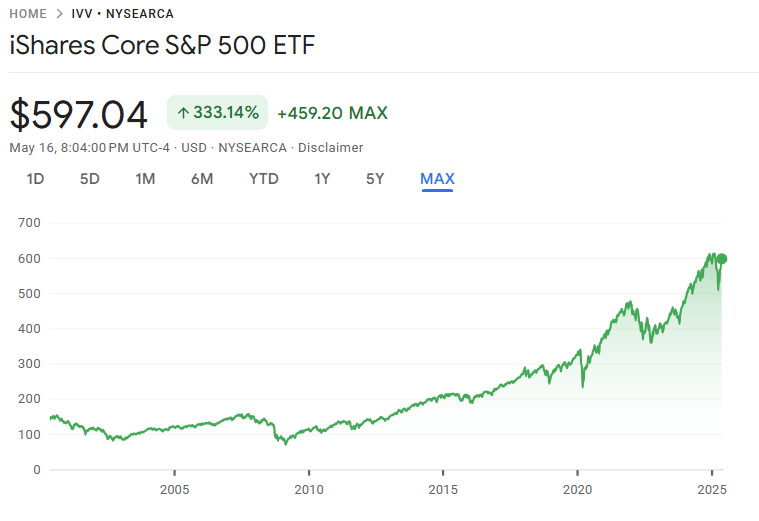
Today, let’s explore IVV (iShares Core S&P 500 ETF) — a quiet performer that offers stability, efficiency, and trust.
If you’re a long-term investor looking for a globally respected, low-cost core holding, this ETF deserves your attention.
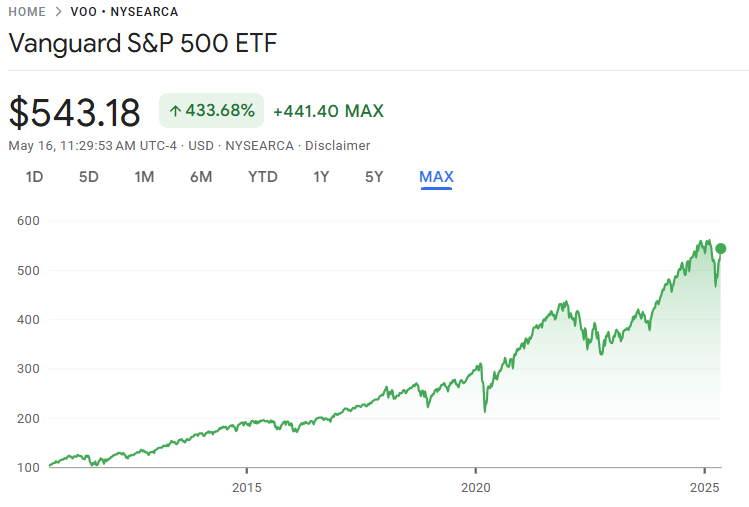
-Historical performance of IVV – Over 333.14% growth since inception (Source: Google Finance)
When most people think of S&P 500 ETFs, names like SPY and VOO come to mind.
But if you’re looking for a fund that combines structural efficiency, institutional trust, and long-term performance,
IVV – the iShares Core S&P 500 ETF deserves serious consideration.
Managed by BlackRock, the world’s largest asset manager, IVV is a no-nonsense ETF that delivers exactly what long-term investors need.
📌 1. Basic Information
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| ETF Name | iShares Core S&P 500 ETF (IVV) |
| Issuer | BlackRock (iShares) |
| Inception Date | May 15, 2000 |
| Underlying Index | S&P 500 Index |
| Expense Ratio | 0.03% |
| Dividend Frequency | Quarterly (Mar, Jun, Sep, Dec) |
| Dividend Yield | ~1.30% (as of May 2025) |
| Share Price | ~$597.04 |
| Average Daily Volume | ~4.5 million shares |
📊 iShares Core S&P 500 ETF Fact Sheet
👉 https://www.ishares.com/us/products/239726/ishares-core-sp-500-etf
✅ 2. Pros & Cons
Let’s break down the key strengths and weaknesses of the IVV ETF in a more practical, real-world context.
✅ Pros
1. Ultra-low expense ratio (0.03%)
IVV has one of the lowest expense ratios on the market — tied with VOO and significantly lower than SPY’s 0.09%. This makes it an excellent vehicle for long-term compounding.
2. Tax-efficient structure (for U.S. residents)
IVV uses an in-kind redemption process, which helps reduce taxable events inside the fund — an advantage particularly relevant to U.S.-based investors.
3. Institutional-grade reliability
IVV is widely trusted by pension funds, university endowments, and large institutional investors, largely due to BlackRock’s reputation and operational scale.
4. Built for modern markets
The ETF is T+1 settlement compatible and structurally optimized for today’s faster, more automated U.S. trading infrastructure.
5. Flexible and modern fund structure
Unlike SPY, which uses an older unit investment trust (UIT) structure, IVV is an open-end fund. This makes it more flexible when it comes to managing dividends, rebalancing, and adapting to regulatory changes.
⚠️ Cons
1. Less brand recognition among retail investors
While institutions love it, IVV doesn’t have the same name recognition as SPY or VOO in mainstream retail circles.
2. Slightly lower liquidity than SPY
Although IVV trades millions of shares daily, it’s still slightly behind SPY in terms of raw liquidity. That could mean marginally wider spreads for short-term traders — though it’s a non-issue for long-term investors.
3. Nearly identical to SPY and VOO
Because all three ETFs track the S&P 500 index almost identically, holding more than one might not meaningfully improve portfolio diversification.
📈 3. Historical Performance (CAGR)
| Timeframe | CAGR |
|---|---|
| 3-Year | ~10.8% |
| 5-Year | ~12.1% |
| 10-Year | ~12.5% |
| Since Inception | +333.14% (as of 2025) |
📊 Google Finance – IVV chart
👉 https://www.google.com/finance/quote/IVV:NYSEARCA
💰 4. Dividend Growth
| Timeframe | Growth Rate |
|---|---|
| 3-Year | ~6.3% |
| 5-Year | ~5.2% |
| 10-Year | ~6.8% |
📊 ETF Channel – IVV dividend history
👉 https://www.etfchannel.com/symbol/ivv/dividends/
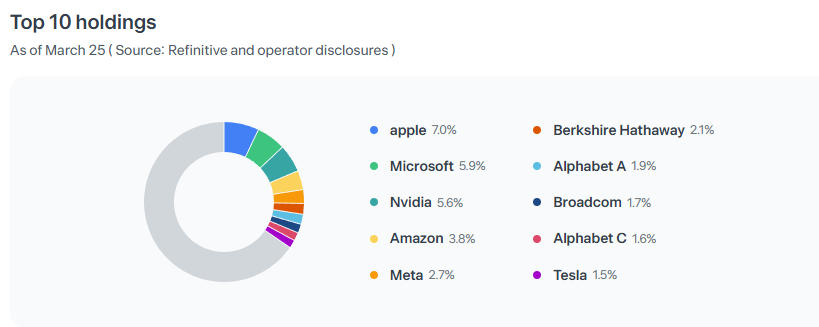
🏗️ 5. Sector Allocation & Top Holdings
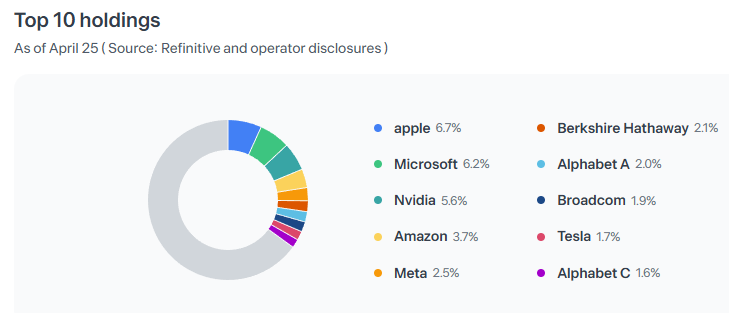
Top 10 Holdings of IVV as of April 2025 (Source: Toss Securities)
Total Holdings: ~500
| Sector | Weight (%) |
|---|---|
| Information Technology | 30.8% |
| Financials | 14.3% |
| Health Care | 10.3% |
| Consumer Discretionary | 10.0% |
| Communication Services | 9.3% |
| Industrials | 8.5% |
| Consumer Staples | 6.2% |
| Energy | 3.2% |
| Utilities | 2.6% |
| Real Estate | 2.1% |
| Materials | 2.0% |
📊 IVV official holdings (BlackRock)
👉 https://www.ishares.com/us/products/239726/ishares-core-sp-500-etf
🔄 6. Rebalancing Frequency & Example
- Schedule: Quarterly (March, June, September, December)
- Managed by: S&P Index Committee
- Implemented by: BlackRock (automatically)
📌 Real Example from Dec 2024:
✅ Added: Apollo Global, Workday, Lennox International
❌ Removed: Catalent, Amentum Holdings, Qorvo
📊 S&P 500 Index Rebalancing Details
👉 https://www.investopedia.com/index-rebalancing-7972596
💬 My Take
IVV doesn’t make headlines — and that’s its strength.
It’s the kind of ETF you don’t have to think about every day.
It quietly tracks the market, minimizes drag, and compounds wealth over time.
And when backed by BlackRock, you get not only low fees, but also institutional trust.
Personally, I chose SPLG for its even lower price per share and greater flexibility for dollar-cost averaging.
But if you’re seeking a high-quality, “set-and-forget” core ETF for your portfolio,
IVV is one of the strongest candidates available — especially for long-term, global investors who prioritize efficiency and stability.
📎 Related Reads
- SPY ETF – The Original S&P 500 Powerhouse
- VOO ETF – Vanguard’s Long-Term Philosophy
- SCHD ETF – Designed for Dividend Growth
💼 Disclaimer
This blog post reflects my personal opinions and investing experience.
It is not intended as financial advice. Please always do your own research or consult with a licensed advisor before making investment decisions.
📌 Sharing Policy
You’re welcome to share this post or quote parts of it — as long as you credit the original source and include a link back to this blog.
Unauthorized copying, pasting, or reposting in full without permission is strictly prohibited.